introduction-to-snmpv3-and-secure-monitoring
SNMPv3 represents a significant improvement over its predecessors by addressing the security shortcomings inherent in SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c. It introduces mechanisms for strong authentication, message integrity, and optional encryption—making it suitable for secure, enterprise-grade network monitoring.
This section outlines the enhancements introduced with SNMPv3, demonstrates how to configure it on network devices, and explains how to interact with SNMPv3-enabled devices using command-line tools.
1 Differences Between SNMPv2c and SNMPv3
| Feature | SNMPv2c | SNMPv3 |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Community strings (plaintext) | User-based (HMAC with SHA/MD5) |
| Encryption | None | Optional (AES, DES) |
| Message Integrity | No | Yes |
| Access Control | Basic (community-based) | Role-based (View-based Access Control Model – VACM) |
| Transport Protocol | UDP | UDP (default), can support TCP |
| Security Model | None | User-based Security Model (USM) |
SNMPv3 introduces the User-based Security Model (USM) and View-based Access Control Model (VACM) to enforce secure and granular access policies.
2 Authentication and Encryption Features
SNMPv3 supports three security levels:
- noAuthNoPriv – No authentication, no privacy (similar to SNMPv2c).
- authNoPriv – Authenticated messages (HMAC-SHA or HMAC-MD5), no encryption.
- authPriv – Authenticated and encrypted messages (HMAC-SHA/HMAC-MD5 + AES/DES encryption).
This flexibility allows administrators to balance performance and security based on environment sensitivity.
3 Configuring SNMPv3 on Routers
Cisco IOS Configuration Example (with authentication and encryption):
R1(config)# snmp-server group SNMPv3Group v3 priv
R1(config)# snmp-server user SNMPv3User SNMPv3Group v3 auth sha MyAuthPass123 priv aes 128 MyPrivPass456
R1(config)# snmp-server location SecureLab
R1(config)# snmp-server contact admin@example.comExplanation:
- SNMPv3User: The username for SNMPv3 access.
- auth sha: Enables authentication using HMAC-SHA.
- priv aes 128: Enables encryption using AES with a 128-bit key.
Verify configuration:
R1# show snmp user
R1# show snmp group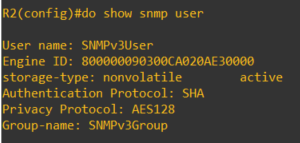
4 Querying SNMPv3 Using CLI Tools
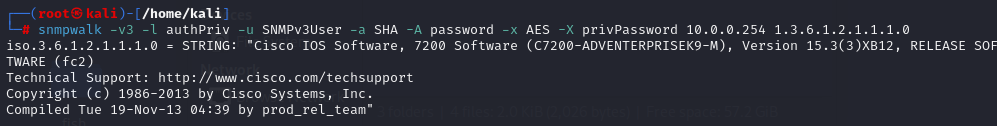
To interact with SNMPv3-enabled devices, use tools like snmpwalk or snmpget, specifying the security model and credentials.
Example – SNMPv3 walk with auth and priv:
snmpwalk -v3 -l authPriv -u SNMPv3User -a SHA -A MyAuthPass123 -x AES -X MyPrivPass456 <device_ip> 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0- -v3: Use SNMP version 3.
- -l authPriv: Security level (authentication and encryption).
- -u: Username.
- -a / -A: Authentication protocol and password.
- -x / -X: Privacy (encryption) protocol and password.