environment-setup
1 User Management
Creating a New User
- Log in as the root or default user.
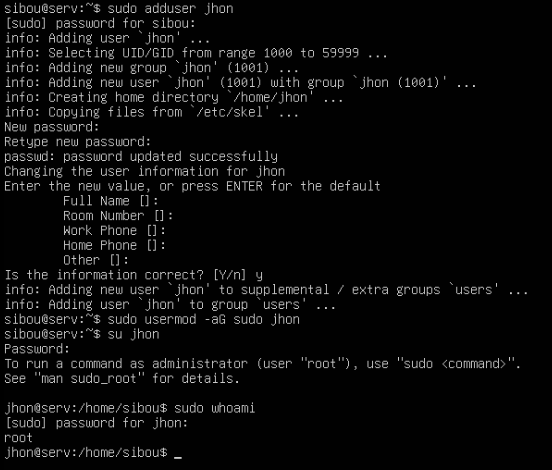
- Create a new user:
sudo adduser <username>
This command creates a new user and prompts you to set a password. The system will also ask for optional user details (full name, room number, etc.).
- Set a password when prompted and confirm it. (for this part, I’ve chosen a weak password from the rockyou.txt wordlist)
Assigning and Managing User Privileges
- Grant sudo privileges to the user:
sudo usermod -aG sudo <username>
usermod modifies a user account. aG sudo adds the user to the sudo group, granting administrative privileges.
- Verify the user’s sudo access:
su - <username> sudo whoami
su -
2 SSH Configuration for Password-Based Authentication
Starting and Validating SSH Service
- Start the SSH Service:
sudo systemctl start ssh - Check the status of SSH:
sudo systemctl status ssh
Displays the status of the SSH service to verify that it’s running.
- Test SSH login from a remote machine:
ssh <username>@<server-ip>
username is the user created earlier.
server-ip is the IP address of the Ubuntu server.
If successful, you should gain access to the server remotely.