amazigh-knew-binary
Challenge Description
You captured traffic from a system believed to be using a covert channel linked to Amazigh resistance communications. But something’s off. The real data isn’t in the content.
Provided Files
Solution
This challenge revolves around timing-based data exfiltration. Upon opening the capture file in Wireshark we observe a consistent stream of HTTP GET requests being sent to a single endpoint.
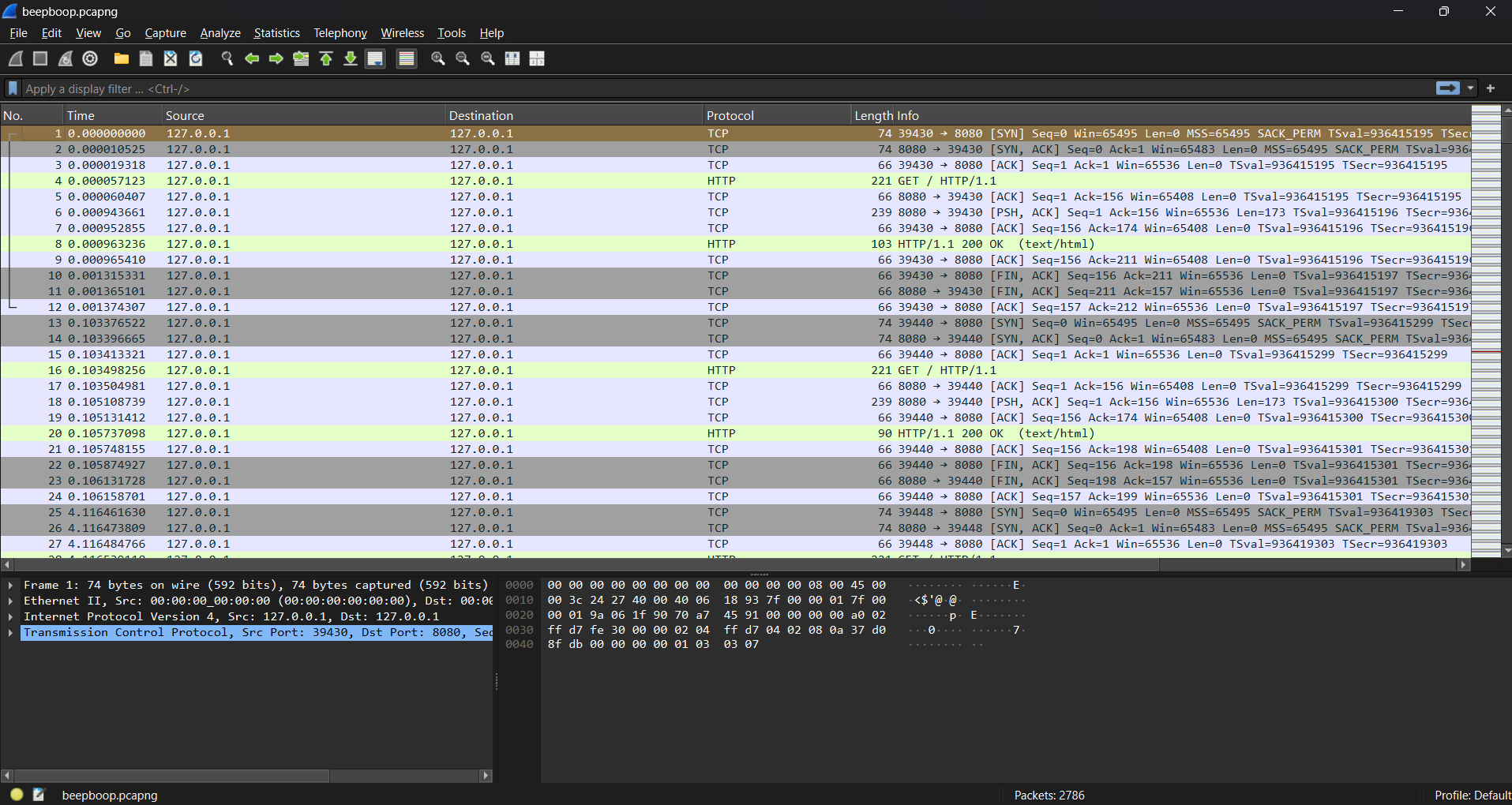
However, unlike most web traffic, this one seems suspiciously empty: there’s no payload, no parameters, and the server replies with simple phrases like:
- “The difference between 1 and 0 is time.”
- “It’s not what was said, but when.”
- “Tifinagh leaves traces in time.”
These messages serve as hints—the payload isn’t in the content, but in timing between requests.
Step 1: Identify the Signal
The PCAP contains multiple HTTP GET requests sent from a client to a local web server (127.0.0.1:8080). Using the following Wireshark display filter helps isolate them:
http.request.method == "GET" && ip.dst == 127.0.0.1We then observe the time deltas between each consecutive request. They appear to alternate between short and long delays:
- Short delay ≈ 0.1 seconds
- Long delay ≈ 4 seconds
This strongly suggests covert binary transmission using timing intervals:
- Short delay = bit 0
- Long delay = bit 1
Step 2: Decode the Timing Channel
To extract the hidden message, we need to:
- Extract timestamps of all valid HTTP GET requests
- Calculate time differences between each request
- Convert these time gaps into bits (0 or 1) using a threshold
- Group bits into bytes (8 bits)
- Convert each byte into its ASCII character
Here is a sample python script that does just that:
from scapy.all import *
import sys
# --- CONFIG ---
SHORT_THRESHOLD = 1 # anything below is considered bit '0'
LONG_THRESHOLD = 3 # anything above is considered bit '1'
TARGET_IP = "127.0.0.1"
TARGET_PORT = 8080
def is_target_http_get(pkt):
return (
pkt.haslayer(IP) and
pkt[IP].dst == TARGET_IP and
pkt.haslayer(TCP) and
pkt[TCP].dport == TARGET_PORT and
pkt.haslayer(Raw) and
pkt[Raw].load.startswith(b"GET")
)
def extract_timestamps(packets):
timestamps = []
for pkt in packets:
if is_target_http_get(pkt):
timestamps.append(pkt.time)
return sorted(timestamps)
def decode_bits(timestamps):
bits = []
for i in range(1, len(timestamps)):
delta = timestamps[i] - timestamps[i - 1]
if delta < SHORT_THRESHOLD:
bits.append('0')
elif delta > LONG_THRESHOLD:
bits.append('1')
# ignore ambiguous delays
return ''.join(bits)
def bits_to_flag(bits):
chars = []
for i in range(0, len(bits), 8):
byte = bits[i:i+8]
if len(byte) == 8:
try:
chars.append(chr(int(byte, 2)))
except ValueError:
chars.append('?')
return ''.join(chars)
def main():
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("Usage: python3 timing_solver_local.py <capture.pcapng>")
sys.exit(1)
capture_file = sys.argv[1]
print(f"[*] Reading {capture_file}...")
packets = rdpcap(capture_file)
print("[*] Extracting relevant HTTP GET timestamps...")
timestamps = extract_timestamps(packets)
if len(timestamps) < 2:
print("[!] Not enough HTTP GET requests found.")
sys.exit(1)
print(f"[*] Found {len(timestamps)} requests.")
bitstream = decode_bits(timestamps)
print(f"[*] Extracted bitstream:\n{bitstream}\n")
flag = bits_to_flag(bitstream)
print(f"[+] Decoded flag: {flag}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()python.exe .\solver.py .\taskfiles\beepboop.pcapng
[*] Reading .\taskfiles\beepboop.pcapng...
[*] Extracting relevant HTTP GET timestamps...
[*] Found 232 requests.
[*] Extracted bitstream:
0101001101100101011000110111010101110010011010010110111001100101011101000111001101111011011101000110100101100110011010010110111001100001011001110110100001011111001100000011000100110001001100000011000100110000001100010011000001111101
[+] Decoded flag: Securinets{tifinagh_01101010}