setting-up-ssl-for-mysql-communication
This section provides an in-depth guide on how to secure communication between a MySQL server and a client by using SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificates. This ensures that data transmitted between the client and server is encrypted, protecting sensitive information from potential eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
By default, MySQL sends traffic in plaintext, which can be intercepted easily. In this tutorial, we will show you how to enable SSL encryption, verify secure connections, and configure your PHP application to use SSL for secure communication with the MySQL database.
1 Enable SSL on the MySQL Server
To enable SSL encryption on your MySQL server, we first need to configure MySQL to generate and use SSL certificates.
- Configure MySQL to Auto-Generate SSL Certificates
SSL certificates are needed for establishing secure connections. MySQL can auto-generate the required certificates. To enable SSL, you will need to modify the MySQL configuration file to specify the location of these certificates.
Start by editing the mysqld.cnf file:
Add the following lines under the [mysqld] section to specify the locations of the SSL certificates:sudo nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
ssl-ca = /var/lib/mysql/ca.pem
ssl-cert = /var/lib/mysql/server-cert.pem
ssl-key = /var/lib/mysql/server-key.pemThese entries point MySQL to the generated certificates, which include the Certificate Authority (CA) certificate, the server’s certificate, and the server’s private key.
- Restart MySQL
Once you’ve updated the configuration file, restart the MySQL service to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart mysql - Verify SSL Activation
To confirm that SSL has been successfully enabled, connect to MySQL and check the status of SSL:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%ssl%';
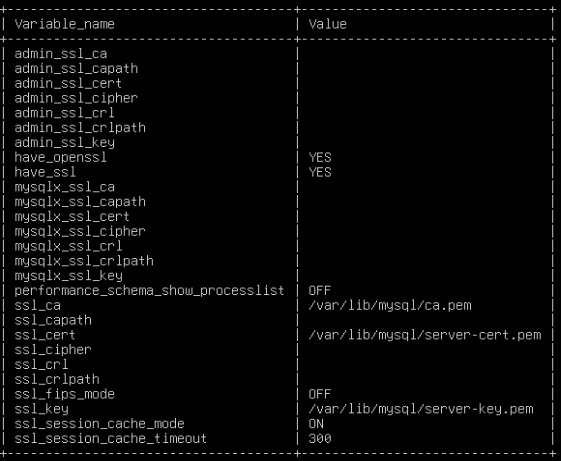
2 Copy the CA Certificate to the Client
To enable the client to communicate securely with the MySQL server, we need to transfer the server’s CA certificate to the client. This certificate is used to verify the authenticity of the MySQL server during the connection handshake.
- Transfer the CA Certificate to the Client
First, create a directory on the client machine to store the certificate:
Then, copy the ca.pem file from the MySQL server to the client machine using scp (secure copy):sudo mkdir -p /etc/mysql/ssl
Replace 192.168.85.139 with the actual IP address or hostname of your MySQL server.sudo cp /var/lib/mysql/ca.pem /home/sibou/ca.pem sudo scp sibou@192.168.85.139:/home/sibou/ca.pem /etc/mysql/ssl/ - Set Permissions
After copying the certificate, ensure it has the appropriate permissions so that it can be accessed by MySQL:
This ensures that the client machine can read the certificate file when establishing the secure connection.sudo chmod 644 /etc/mysql/ssl/ca.pem
3 Configure the MySQL Client to Use SSL
Now that SSL is enabled on both the server and the client, we need to configure the MySQL client to use SSL when connecting to the server.
- Connect to the MySQL Server Using SSL
To establish a secure connection from the MySQL client to the server, you must use the —ssl-ca flag to specify the location of the CA certificate and —ssl-mode=REQUIRED to enforce SSL encryption:
Replace mysql_server_ip with your MySQL server’s IP address and ssl_user with the MySQL username.mysql -h mysql_server_ip -u ssl_user -p --ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/ssl/ca.pem --ssl-mode=REQUIRED - Verify the SSL Connection
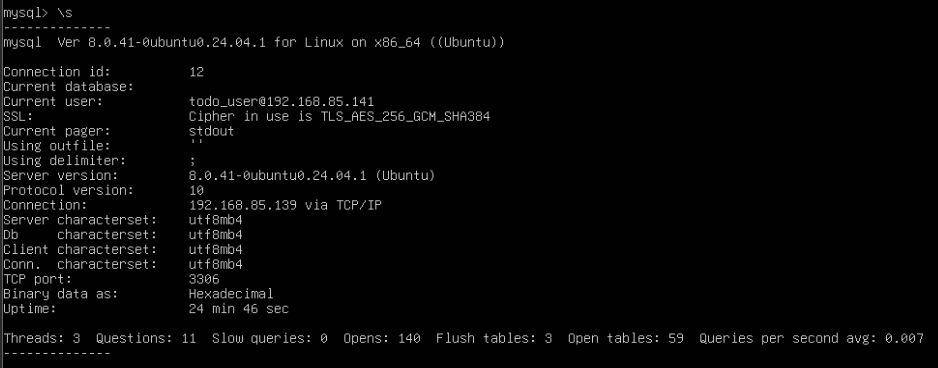
After successfully connecting to the MySQL server, verify that the SSL connection is active by typing the following command in the MySQL client:
This will show detailed information about the current session, including SSL status. You should see a line similar to the following:\s
This confirms that the connection is encrypted using SSL.SSL: Cipher in use
4 Configure PHP to Use SSL for MySQL Connections
In your PHP application, you need to configure the MySQL connection to use SSL for secure communication. To do this, update your db.php (or equivalent) database connection file.
- Modify the db.php File Use the following template to modify your db.php file. This configuration will include the necessary SSL options for the PDO connection. Make sure to replace the paths to your certificates with the actual file paths on your server.
?php
session_start();
$host = "192.168.85.139"; // Remote MySQL server IP
$user = "todo_user"; // Remote MySQL user
$password = "password"; // User password
$dbname = "todo_db"; // Database name
// Path to SSL CA certificate (copied from MySQL server)
$ssl_ca = "/etc/mysql/ssl/ca.pem";
try {
$dsn = "mysql:host=$host;dbname=$dbname;charset=utf8mb4";
// Add SSL configuration to options
$options = [
PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_SSL_CA => $ssl_ca,
PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_SSL_VERIFY_SERVER_CERT => false, // Disable for self-signed certs
PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE => PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION,
PDO::ATTR_DEFAULT_FETCH_MODE => PDO::FETCH_ASSOC
];
$pdo = new PDO($dsn, $user, $password, $options);
} catch(PDOException $e) {
die("Database Connection Failed: " . $e->getMessage());
}
?>